Generating types and accessors
By default, types are generated with their short name (without namespacing). For example, the following diagram:
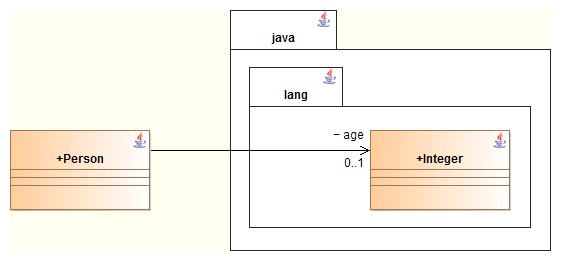
will lead to the generation of the following code for the association of the "Age" role in the "Person" class :
private Integer age;
However, it remains possible to generate the association type with its full name by setting the {JavaFullName} tagged value on the navigable association. This way, the following diagram:
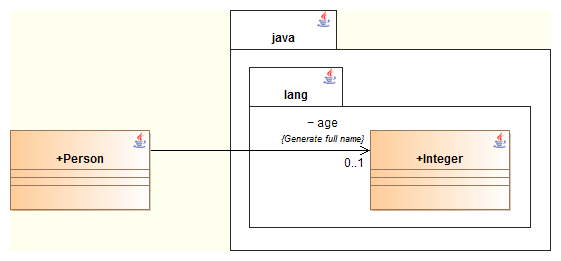
will lead to the generation of this code :
private java.lang.Integer age;
The above rule applies to the generation of navigable associations, attributes, method parameters, generalizations and implementations.
The generation of Java code is based on a UML model, extended by notes and tagged values specific to Java, in order to generate all the code for Java classes.
This generation can be parameterized to a high level, using the following mechanisms:
-
Java generation parameters provide general generation options
-
the Java customization file allows you to modify the mapping of types.
Defining Java annotations
Java annotations are defined in the "Java annotation definition" window.
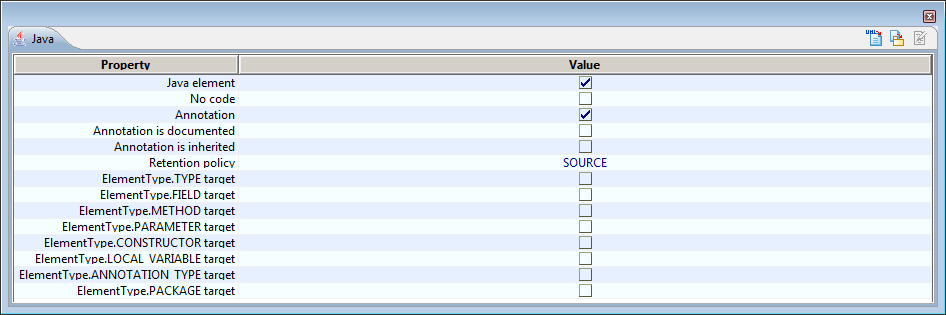
This window, accessible by launching the "Edit properties" command on a class stereotyped JavaAnnotation, defines all options available on the annotation definition.
| Name | Function of the annotation |
|---|---|
Annotation is documented |
Specifies whether the annotation is documented. Corresponds to the @Documented annotation type. |
Annotation is inherited |
Specifies whether the annotation is documented. Corresponds to the @Inherited annotation type. |
Retention |
Specifies the retention policy of the annotation. Corresponds to the @Retention annotation type. |
Annotation target |
Specifies the types of elements where the annotation is applicable. Corresponds to the @Target annotation type. |