The Java Architect module comes with a bunch of services ready to be called from other modules or Jython scripts in Modelio.
They are commonly called peer services.
Peer services
Here is the actual interface defining the peer services:
public interface IJava ArchitectPeerModule extends IPeerModule {
/**
* The module's actual name, often used as an identifier when looking for MDA annotations by name.
*/
public static final String MODULE_NAME = "Java Architect";
/**
* Generate .java source files from the given elements, recursively.
* A transaction is opened, committed at the end or rollbacked in case of error.
* @param javaElements the elements to generate.
* @param progress a progress monitor. Can be null.
* @return the operation report. If it contains errors, the generation failed.
*/
Report generateCode(Collection javaElements, IModelioProgress progress);
/**
* Generate module-info.java source files from the given java modules.
* @param jpmsModules the modules to generate.
* @param progress a progress monitor. Can be null.
* @return the operation report. If it contains errors, the generation failed.
*/
Report generateModuleInfo(Collection jpmsModules, IModelioProgress progress);
/**
* Update the model from existing .java source files, recursively.
* A transaction is opened, committed at the end or rollbacked in case of error.
* @param javaElements the elements to update.
* @param progress a progress monitor. Can be null.
* @return the operation report. If it contains errors, the generation failed.
*/
Report updateCode(Collection javaElements, IModelioProgress progress);
/**
* Update the model from existing .java source files, recursively.
* A transaction is opened, committed at the end or rollbacked in case of error.
* @param jpmsModules the modules to update.
* @param progress a progress monitor. Can be null.
* @return the operation report. If it contains errors, the generation failed.
*/
Report updateModuleInfo(Collection jpmsModules, IModelioProgress progress);
/**
* Update all the accessors corresponding to this element (type, card, name...).
* According to the feature's access mode, accessors might be created or deleted in the model.
* @param element The element to synchronize accessors from.
*/
void updateAccessors(StructuralFeature element);
/**
* Compute the fully qualified java name of an element, taking aliases into account.
* @param elt a model element.
* @return a fully qualified name.
*/
String getFullName(ModelElement elt);
/**
* @param elt a model element.
* @return the absolute path of the java file corresponding to the element. Might be null if the element is not a java element or "no code".
*/
Path getFilePath(ModelElement elt); |
|
Java Architect does not open report dialogs when a peer service is called, instead most services return an org.modelio.api.module.report.Report instance containing errors and warnings. See Modelio’s Javadoc for more information. |
From a Jython script
Jython scripts can be used in a lot of ways in Modelio and it is perfectly possible to call module peer services in them.
For example, use a script to generate all the Java code from a project:
from org.modelio.api.modelio import Modelio
from org.modelio.metamodel.mda import Project
from java.util import HashSet
elements = HashSet()
for root in modelingSession.getModel().getModelRoots():
if isinstance(root, Project):
for p in root.getModel():
elements.add(p)
# Access the peer services
moduleService = Modelio.getInstance().getModuleService()
peerModule = moduleService.getPeerModule("Java Architect")
if peerModule:
# Generate the code
print "Generating", elements.size(), "elements"
report = peerModule.generateCode(elements, None)
# Handle the report
print "Generation done - Errors:",report.hasErrors(), "- Warnings:",report.hasErrors()|
|
This is particularly useful to automate code generation, using Modelio in batch mode with a Jython script! |
From a module
To use peer services in another module, it is necessary to make the Java Architect’s code available in it.
First, add a dependency between the modules:
-
Open your module development project.
-
In the model, select your
 Modelio Studio module.
Modelio Studio module. -
From the contextual menu (rightclick) execute the
 Modelio Studio → Create element →
Modelio Studio → Create element → 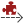 Module Dependency command.
Module Dependency command. -
The command will pop the following GUI, just select Java Architect in it.
|
|
With this dependency, you make sure your module won’t start in Modelio unless Java Architect is started too. At Java code level, Modelio also makes your module’s classloaded contain Java Architect’s classes at runtime. |
In order to actually use these classes, you have to add a compilation dependency. Follow the following steps:
-
In the model, select your
 Modelio Studio module again.
Modelio Studio module again. -
From the contextual menu (rightclick) execute the
 Modelio Studio → Create element →
Modelio Studio → Create element →  Maven Dependency command.
Maven Dependency command. -
The command will pop the following GUI:
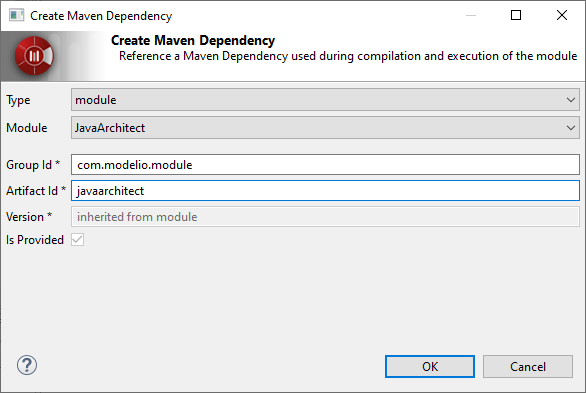
-
Fill the fields:
-
Type: module
-
Maven Group Id: com.modelio.module
-
Maven Artifact Id: javaarchitect
-
Version is automatically filled from the Java Architect deployed in your module development project.
-
-
In the model, select your
 Modelio Studio module again.
Modelio Studio module again. -
From the contextual menu (rightclick) execute the
 Modelio Studio →
Modelio Studio →  Generate/Package module command.
Generate/Package module command.
|
|
At this step, the generated pom.xml contains a maven dependency on Java Architect, making it possible to use its classes. |
All that remains is to use the peer service you need! For example generate code:
public void generateCode(final List selectedElements, final IModule module) {
IModuleContext moduleContext = module.getModuleContext();
IModuleService moduleService = moduleContext.getModelioServices().getModuleService();
// Access the peer services
IJava ArchitectPeerModule peerModule = moduleService.getPeerModule(IJava ArchitectPeerModule.class);
// Generate the code
Report report = peerModule.generateCode(selectedElements, null);
// Open the report dialog if necessary
if (!report.getEntries().isEmpty()) {
IModelioServices modelioServices = moduleContext.getModelioServices();
Shell current = Display.getCurrent().getActiveShell();
ReportDialog dlg = new ReportDialog(current, moduleContext.getModelingSession(), modelioServices.getNavigationService(), report);
dlg.open();
}
}